Can Smart Diabetes Control Transform Lives?
In today’s challenging world, many individuals wonder how they can reclaim their health and live a fulfilling life. Diabetes Control emerges as a beacon of hope, offering practical solutions to manage and prevent diabetes effectively. Do you ever ask yourself, “How can I take charge of my health?” This article invites you to embark on a journey toward understanding diabetes and applying clear, actionable steps that promote well‐being. With a friendly and empathetic tone, we guide you through types, symptoms, causes, and the best ways to prevent and treat this condition.
Table of contents
- Can Smart Diabetes Control Transform Lives?
- 1. What Is Diabetes and Why Is Smart Diabetes Control Essential?
- 2. How Do the Types of Diabetes Differ Under Smart Diabetes Control?
- 3. What Are the Common Symptoms That Signal a Need for Smart Diabetes Control?
- 4. Why Does Diabetes Occur? What Causes Demand Smart Diabetes Control?
- 5. How Can You Prevent Diabetes with Smart Diabetes Control?
- 6. What Treatment Options Are Available for Diabetes and How Do They Relate to Smart Diabetes Control?
- 7. How Can You Effectively Implement Smart Diabetes Control in Daily Life?
- 8. What Does Research Say About Smart Diabetes Control and Future Directions?
- 9. How Can You Reflect on Your Journey Toward Smart Diabetes Control?
- Conclusion
1. What Is Diabetes and Why Is Smart Diabetes Control Essential?
Diabetes is a complex metabolic condition that significantly impacts the body’s ability to process glucose. Therefore, understanding it becomes crucial for anyone determined to embrace Diabetes Control. Fundamentally, diabetes disrupts the harmony between insulin production and blood sugar regulation, leading to potential complications if not managed properly.
Key Points:
- Diabetes occurs when the body cannot produce or properly utilize insulin.
- It affects millions worldwide, prompting urgent calls for proactive Diabetes Control.
- The condition can lead to severe complications such as heart disease, kidney failure, and vision problems if ignored.
Moreover, modern research highlights that early detection and consistent management are vital. Consequently, by practicing Diabetes Control, individuals empower themselves to reduce risks and enjoy a vibrant lifestyle.
2. How Do the Types of Diabetes Differ Under Smart Diabetes Control?
Understanding the various forms of diabetes is fundamental. Each type demands a tailored approach to Smart Diabetes Control. Let’s explore the primary categories:
2.1 What Defines Smart Diabetes Control in Type 1 Diabetes?
Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune condition that usually develops in childhood or adolescence. In this form, the body’s immune system mistakenly destroys insulin-producing cells.
- Characteristics:
- Rapid onset: Symptoms develop quickly.
- Insulin dependency: Patients require regular insulin injections.
- Management focus: Achieving Diabetes Control involves continuous monitoring and timely insulin administration.
For instance, many young individuals adapt by integrating insulin therapy with dietary and physical activity adjustments.
2.2 What Defines Smart Diabetes Control in Type 2 Diabetes?
Type 2 diabetes, the most common form, primarily results from insulin resistance and gradual insulin deficiency. Lifestyle factors and genetic predisposition contribute to its onset.
- Characteristics:
- Slow progression: Symptoms emerge over time.
- Lifestyle influence: Diet, exercise, and weight play pivotal roles.
Notably, adopting a balanced diet and regular physical activity enhances Diabetes Control and minimizes the disease’s progression.
2.3 How Does Gestational Diabetes Require Smart Diabetes Control?
Gestational diabetes appears during pregnancy and usually resolves after childbirth. However, it demands careful Smart Diabetes during the pregnancy period.
- Characteristics:
- Temporary condition: Occurs in pregnant women.
- Increased risk: Can affect both mother and baby if not managed.
- Management focus: Nutritional guidance and regular blood sugar checks are essential.
Therefore, maintaining sugar levels ensures a safer pregnancy experience and lowers the future risk of developing Type 2 diabetes.
3. What Are the Common Symptoms That Signal a Need for Smart Diabetes Control?
Recognizing diabetes symptoms early is a crucial step toward achieving blood sugar levels. Early detection not only prevents complications but also empowers you to take control of your health journey.
3.1 Which Symptoms Should You Watch For?
- Frequent urination: Increased urination results from the body trying to eliminate excess glucose.
- Excessive thirst: As a result of dehydration, you may feel unquenchable thirst.
- Fatigue: Reduced energy levels indicate the body’s struggle to use glucose properly.
- Blurred vision: High blood sugar levels can affect the eyes.
- Unexplained weight loss or gain: Metabolic imbalances may lead to unexpected changes in body weight.
Additionally, you may experience slow wound healing, increased inflammation, and tingling in your extremities. By identifying these symptoms, you’ve taken the first step toward controlling your diabetes.
3.2 How Do These Symptoms Impact Daily Life?
Each symptom affects your daily routine in different ways. For example:
- Frequent urination disrupts sleep and work patterns.
- Fatigue hinders your ability to enjoy daily activities.
- Blurred vision makes routine tasks challenging.
Recognizing and addressing these early signs encourages prompt medical advice, paving the way for effective controlling your diabetes.
4. Why Does Diabetes Occur? What Causes Demand Smart Diabetes Control?
The causes of diabetes are multifaceted, necessitating a comprehensive approach to controlling it. Both genetic and environmental factors contribute to the disease’s development.
4.1 What Are the Genetic and Lifestyle Risk Factors?
- Genetic predisposition: A family history increases risk.
- Obesity: Excess body weight, particularly around the abdomen, contributes significantly.
- Sedentary lifestyle: Lack of exercise accelerates insulin resistance.
- Poor diet: High consumption of processed foods, sugars, and unhealthy fats can trigger the condition.
- Stress: Chronic stress disrupts metabolic balance.
For example, studies have shown that individuals with a sedentary lifestyle who consume unhealthy diets face a higher risk. Therefore, embracing Smart Diabetes Control involves addressing these lifestyle factors directly.
4.2 How Do Environmental Factors Contribute?
- Pollution and chemicals: Exposure to certain toxins can affect metabolic processes.
- Socioeconomic factors: Access to healthy food and medical care often influences diabetes prevalence.
- Urbanization: Rapid urban growth often leads to lifestyle changes that heighten the risk.
Hence, adopting Smart Diabetes Control means acknowledging both personal and environmental elements that contribute to the disease.
5. How Can You Prevent Diabetes with Smart Diabetes Control?
Preventing diabetes hinges on proactive measures and informed lifestyle choices. Smart Diabetes Control is not just about treatment—it’s also about prevention.
5.1 What Lifestyle Changes Can Boost Smart Diabetes Control?
- Balanced Diet: Consume whole grains, lean proteins, vegetables, and fruits.
- For instance, plan meals that include low glycemic index foods.
- Regular Exercise: Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate physical activity daily.
- Weight Management: Maintain a healthy weight through diet and exercise.
- Stress Reduction: Practice mindfulness, yoga, or meditation to manage stress levels.
- Regular Monitoring: Check your blood sugar levels and seek medical advice promptly if anomalies occur.

5.2 What Practical Steps Can You Implement?
Consider this actionable plan for Smart Diabetes Control:
- Plan Meals: Create weekly menus that emphasize nutritional balance.
- Schedule Exercise: Incorporate physical activities into your daily routine.
- Use Technology: Leverage mobile apps and wearable devices to track health metrics.
- Join Support Groups: Engage with communities that focus on healthy living.
Additionally, many research studies, including those from the World Health Organization (WHO) and Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), support these strategies. Their findings underline the effectiveness of Smart Diabetes Control in reducing risk factors and improving overall health.
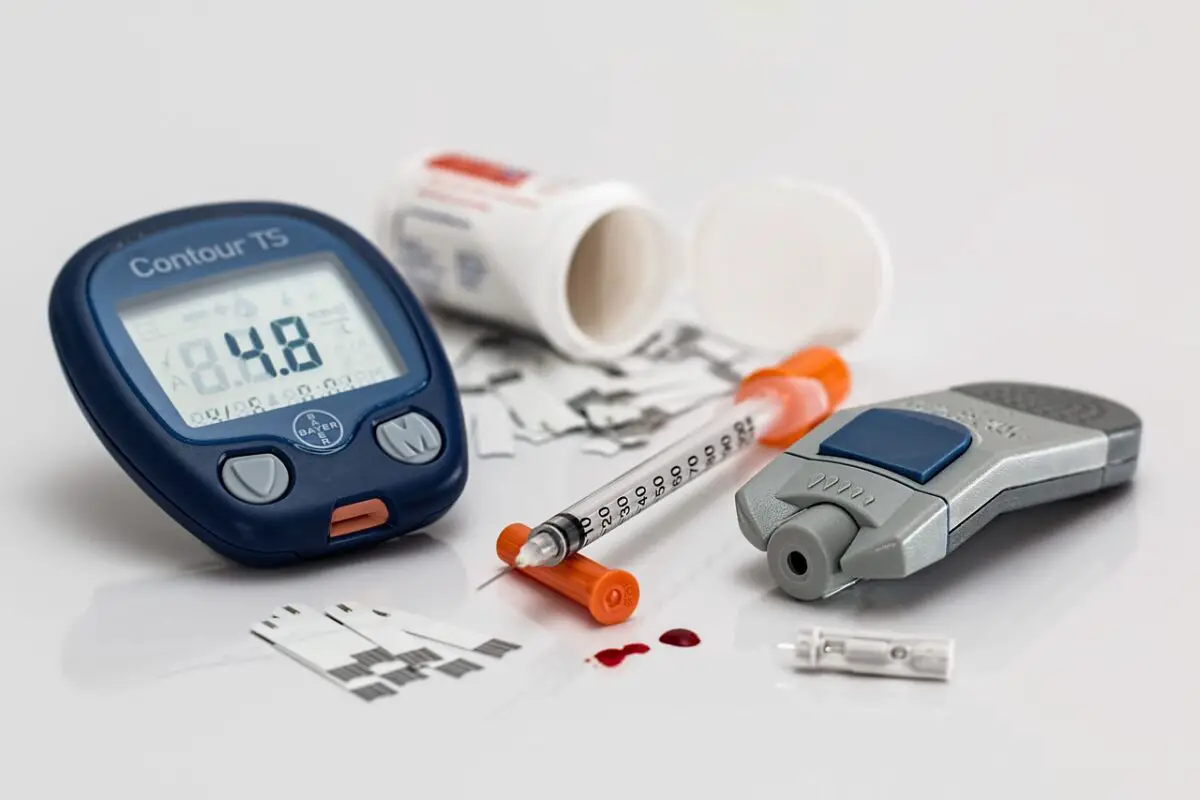
6. What Treatment Options Are Available for Diabetes and How Do They Relate to Smart Diabetes Control?
Effective treatment of diabetes requires a comprehensive approach that integrates medication, lifestyle changes, and continuous monitoring. Embracing Smart Diabetes Control means tailoring your treatment to your unique needs.
6.1 What Medications Support Smart Diabetes Control?
- Insulin Therapy: Essential for Type 1 diabetes and sometimes for Type 2.
- Oral Medications: Drugs like metformin help regulate blood sugar in Type 2 diabetes.
- Non-insulin Injectables: These medications can improve glucose regulation.
6.2 How Do Lifestyle Modifications Enhance Treatment?
- Dietary Adjustments: Adopt a low-carbohydrate, high-fiber diet.
- Exercise Programs: Regular activity improves insulin sensitivity.
- Stress Management: Techniques such as deep breathing contribute to better metabolic control.
6.3 Can You See a Comparison?
Below is a simple table comparing treatment approaches that embody Smart Diabetes Control:
| Aspect | Type 1 Diabetes | Type 2 Diabetes | Gestational Diabetes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Primary Approach | Insulin injections | Diet, exercise, oral medications | Nutritional guidance, blood monitoring |
| Lifestyle Role | Essential for overall health | Critical to manage progression | Key for temporary management |
| Monitoring Frequency | Multiple times daily | Regular monitoring | Frequent during pregnancy |
| Long-term Management | Lifelong commitment | Can sometimes be managed with lifestyle changes | Focused on pregnancy period |
This table clearly illustrates how Diabetes Control adapts to various forms of diabetes, emphasizing tailored approaches to treatment and management.
7. How Can You Effectively Implement Smart Diabetes Control in Daily Life?
Real-world application of Smart Diabetes Control requires dedication, practical planning, and consistent follow-up. The following steps outline a comprehensive guide for integrating these practices into your everyday routine.
7.1 What Practical Steps Should You Take Today?
- Educate Yourself:
- Research reliable sources and attend educational seminars on diabetes.
- Familiarize yourself with the latest findings from reputable institutions like the American Diabetes Association (ADA).
- Develop a Personalized Plan:
- Consult healthcare professionals to tailor a plan that suits your unique needs.
- Set realistic goals for diet, exercise, and blood sugar monitoring.
- Create a Supportive Environment:
- Involve family and friends in your journey.
- Join online forums or local groups to share experiences and advice.
7.2 Which Daily Practices Enhance Smart Diabetes Control?
- Monitor Your Health:
- Use digital tools to track blood sugar levels, physical activity, and dietary intake.
- Stay Active:
- Integrate activities such as brisk walking, cycling, or swimming into your schedule.
- Plan Nutritious Meals:
- Prepare balanced meals that reduce processed sugars and emphasize whole foods.
- Reflect and Adjust:
- Regularly review your progress and modify your routine as necessary.
For example, you may decide to take a 30-minute walk after dinner every day, which not only boosts physical fitness but also contributes to Smart Diabetes Control. Additionally, scheduling periodic health assessments helps in making informed decisions about your treatment plan.
7.3 How Can Technology Assist in Smart Diabetes Control?
Modern technology plays a significant role in supporting diabetes management. Consider these innovative tools:
- Mobile Applications: Apps track dietary intake, exercise, and blood sugar levels.
- Wearable Devices: Smartwatches and fitness bands provide real-time feedback on your activity levels.
- Telemedicine: Virtual consultations ensure continuous support from healthcare professionals.
Thus, by integrating technology, you enhance your ability to maintain Smart Diabetes Control and adapt quickly to any changes in your health.
8. What Does Research Say About Smart Diabetes Control and Future Directions?
Current research continues to shed light on diabetes management and prevention. Therefore, staying updated with new developments becomes an integral part of Smart Diabetes Control.
8.1 Which Studies Highlight Effective Smart Diabetes Control Strategies?
- Longitudinal Studies:
- Research from various institutions demonstrates that individuals who adhere to lifestyle changes significantly reduce their risk of complications.
- Clinical Trials:
- Trials comparing different medications and lifestyle interventions show promising results when combined with Smart Diabetes Control.
For example, one study reported that participants who engaged in regular physical activity and dietary modifications experienced a 30% reduction in diabetes-related complications over a 5-year period. This finding emphasizes that Smart Diabetes Control is not just theoretical—it delivers measurable improvements.
8.2 What Future Trends Can Boost Smart Diabetes Control?
- Personalized Medicine:
- Advancements in genetic profiling may soon allow for tailored treatment strategies.
- Artificial Intelligence:
- AI-driven platforms can predict blood sugar fluctuations, helping you adjust your routines proactively.
- Community Health Initiatives:
- Increased public awareness and support programs are likely to make Smart Diabetes Control accessible to a broader audience.
Additionally, policymakers and healthcare providers are focusing on preventive measures, ensuring that future strategies for Smart Diabetes Control are innovative, inclusive, and effective.
9. How Can You Reflect on Your Journey Toward Smart Diabetes Control?
Taking charge of diabetes management is a dynamic process that evolves with time. Ask yourself, “What progress have I made today?” Embracing Smart Diabetes Control means continuously assessing your health, celebrating small victories, and staying motivated even when challenges arise.
9.1 How Do You Stay Motivated?
- Set Achievable Goals:
- Break your journey into small, measurable steps.
- Reward Yourself:
- Celebrate milestones by treating yourself to a favorite, healthy activity.
- Keep a Journal:
- Document your progress and reflect on changes in your health.
9.2 What Role Does Community Play in Smart Diabetes Control?
- Engage with Others:
- Share your experiences with support groups or online communities.
- Seek Professional Guidance:
- Maintain regular check-ins with your healthcare provider.
- Stay Informed:
- Participate in local workshops or webinars that focus on diabetes care.
These interactive practices not only bolster your confidence but also solidify your commitment to Smart Diabetes Control. As you implement these strategies, you become part of a global movement dedicated to living a healthier, happier life.
Conclusion
In summary, diabetes presents a complex challenge that demands proactive and comprehensive management. By understanding the types, symptoms, causes, and treatment strategies, you equip yourself to embrace Smart Diabetes Control. Throughout this article, we have explored actionable steps and practical tips that guide you in transforming your daily routines, empowering you to overcome obstacles and celebrate every small success.
Are you ready to embark on your journey toward better health? Remember, every step you take towards Smart Diabetes Control brings you closer to a life filled with energy, confidence, and hope. Engage with your community, leverage technology, and continuously educate yourself. Your commitment today sets the foundation for a brighter, healthier tomorrow.
Source Article Links
- World Health Organization – Diabetes Fact Sheet
- Link: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/diabetes
- Date: Updated regularly (Accessed March 2025)
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention – Diabetes Basics
- Link: https://www.cdc.gov/diabetes/basics/diabetes.html
- Date: Updated regularly (Accessed March 2025)
- American Diabetes Association – Diabetes Overview
- Link: https://www.diabetes.org/diabetes
- Date: Updated regularly (Accessed March 2025)
Studies/Statistics/Experiments
- Diabetes Prevention Program (DPP) Research Group Study
- Link: https://www.niddk.nih.gov/about-niddk/research-areas/diabetes/diabetes-prevention-program-dpp
- Date: Originally published in 2002; data are continually referenced
- Lifestyle Interventions and Reduction in Diabetes-Related Complications
- Link: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4008797/
- Date: (Access details on the article page; typically updated as part of ongoing research)
Image Resources:






